Amino Acid Liver Protein . the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. In all mammals, this organ.
from www.dreamstime.com
the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. In all mammals, this organ. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals.
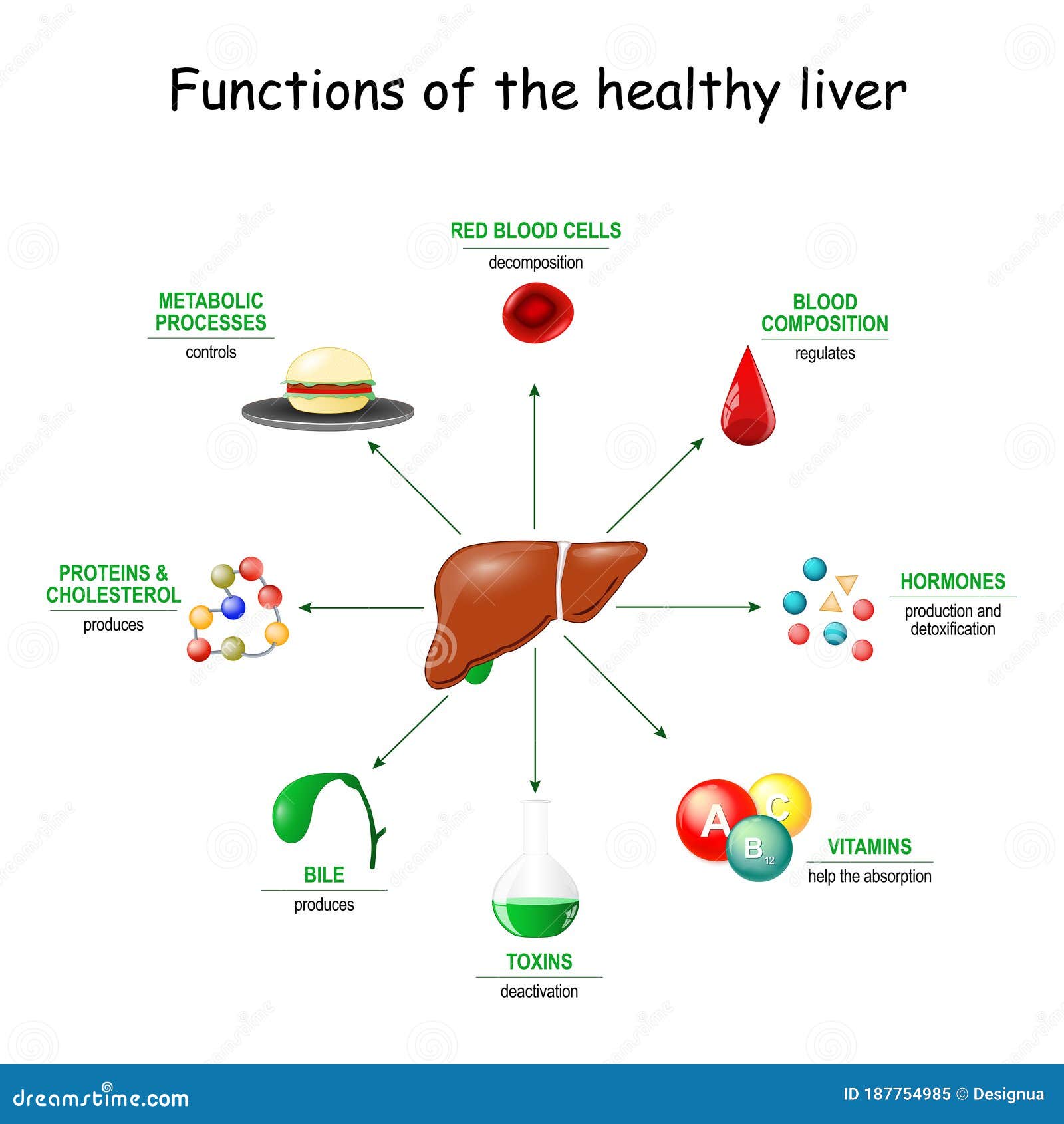
Functions of the Healthy Liver Stock Vector Illustration of icon
Amino Acid Liver Protein the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. In all mammals, this organ. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals.
From fattyliverdisease.com
Essential Amino Acids For Liver Support Fatty Liver Disease Amino Acid Liver Protein liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. the branched chain. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.dreamstime.com
Functions of the Healthy Liver Stock Vector Illustration of icon Amino Acid Liver Protein the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. liver is an important organ. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.researchgate.net
Amino acid concentrations in the liver. Download Scientific Diagram Amino Acid Liver Protein learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. liver. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From journals.physiology.org
Branchedchain amino acids alter cellular redox to induce lipid Amino Acid Liver Protein liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. In all. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
4.6 Protein Uptake, Absorption, Transport & Liver Uptake Nutrition Amino Acid Liver Protein In all mammals, this organ. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. the. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.wjgnet.com
Structural changes of proteins in liver cirrhosis and consequential Amino Acid Liver Protein the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From pocketdentistry.com
The metabolism of proteins and amino acids Pocket Dentistry Amino Acid Liver Protein liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. In all mammals, this organ. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. the. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From study.com
Proteins & Amino Acids Formation, Structures & Sources Lesson Amino Acid Liver Protein the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. specifically, we. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From education.med.nyu.edu
AMINO ACID METABOLISM INTRODUCTION Amino Acid Liver Protein this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. In all mammals, this organ. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. the. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From doctorlib.info
Protein, Peptide, and AminoAcid Absorption Nutrient Digestion and Amino Acid Liver Protein specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. liver is an important. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From docslib.org
The Role of Amino Acids in Liver Protein Metabolism Under a High Amino Acid Liver Protein the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 2 from The role of amino acids in liver protein metabolism under Amino Acid Liver Protein In all mammals, this organ. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 1 from The role of amino acids in liver protein metabolism under Amino Acid Liver Protein In all mammals, this organ. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.anaesthesiajournal.co.uk
Metabolic functions of the liver Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine Amino Acid Liver Protein the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. learn how the liver synthesises, degrades and catabolises amino acids and proteins, and how it removes ammonia through the urea cycle. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. In all mammals,. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.researchgate.net
SIFT Results for Amino Acid Variants of Protein Involved in Human Liver Amino Acid Liver Protein the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. In all mammals, this organ. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. this chapter. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From eduinput.com
Role Of The Liver In Digestion Amino Acid Liver Protein liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. the liver plays a central role in amino acid (aa) metabolism in humans and other animals. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 16 from The role of amino acids in liver protein metabolism Amino Acid Liver Protein the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. liver is an important organ for protein synthesis, degradation and detoxification as well as amino acid. specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. this chapter reviews the metabolic. Amino Acid Liver Protein.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 2 from The role of amino acids in liver protein metabolism under Amino Acid Liver Protein specifically, we demonstrate that increasing extracellular amino acids beyond the nutritional need of hlcs and hepg2 cells induces. the branched chain amino acids (bcaas), valine (val), leucine (leu) and isoleucine (ile), are essential amino acids. this chapter reviews the metabolic functions and significance of amino acids (aas) in the liver of humans. the liver plays a. Amino Acid Liver Protein.